Unlock the Power of Gut Health

Why It Matters
The good bacteria in your gut help break down food, absorb nutrients, and protect against harmful germs. This is why a healthy gut microbiome is key to staying healthy*

Why It Matters
The good bacteria in your gut help break down food, absorb nutrients, and protect against harmful germs. This is why a healthy gut microbiome is key to staying healthy*
The Symbiotic Trio →
-
Prebiotics (fiber)
Non-digestible fibers that feed probiotics, helping them thrive. Without prebiotics, probiotics (the actual bacteria cultures) can't survive. Examples include whole grains, garlic, bananas, and many greens.*
-
Probiotics (bacteria)
Live bacteria that help balance your gut microbiome. Often called ''good'' bacteria, probiotics have been shown to support not only digestion but also immunity, inflammation, mental health, skin health and some chronic diseases.*
-
Postbiotics (acids & enzymes)
Byproducts of the bacteria consuming the fiber, producing acids and enzymes. They strengthen the gut barrier, modulate the immune system, and may help with allergies, heart health, blood sugar levels, and even auto-immune disorders.*

The Magic of Natural Fermentation
Fermented foods like kefir, kombucha, kimchi and sauerkraut, are all rich in probiotics, supporting gut bacteria balance, digestion, and immunity.
They also produce postbiotics like fatty acids and enzymes, nourishing the gut lining and enhancing overall physical and mental well-being.
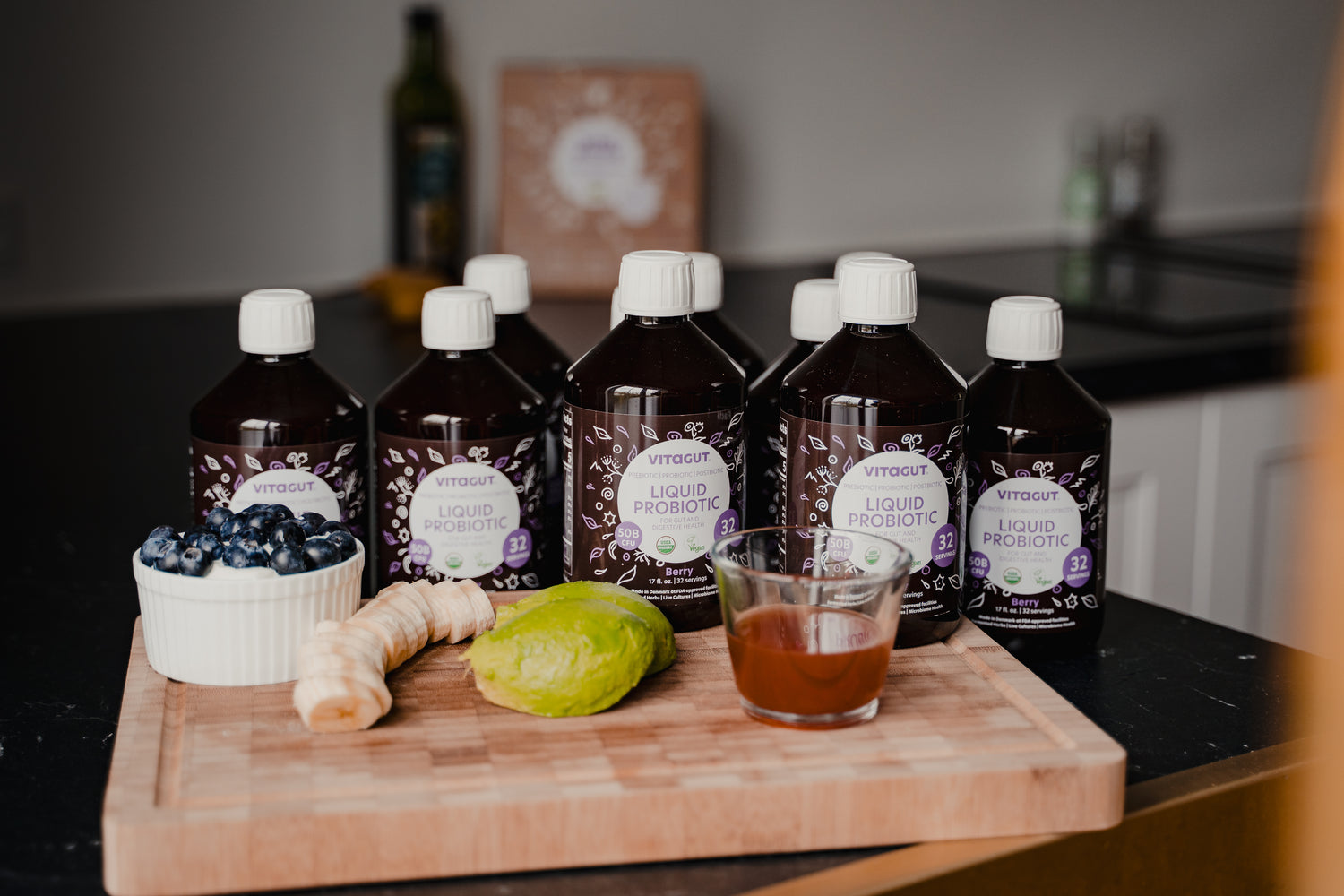

All-In-One Gut Health Drink
VITAGUT features an organic, GMO-free blend of 19 fermented herbs and 8 clinically studies bacteria cultures.
Live, active and fully viable bacteria cultures make our drink a complete gut health optimizer, with both PREBIOTICS, PROBIOTICS, and POSTBIOTICS!

Fuel Your Gut, Transform Your Health
Your gut microbiome impacts nearly every aspect of your overall well-being, from physical vitality to mental clarity.
With the right gut fuel (food), you can literally nourish your way to a healthier body and mind.
Collapsible content
Our Sources
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10001679/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8953587/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10146621/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10334151/ , https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8001875/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6021588/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9499173/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10384867/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9903080/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29762266/

Invest in your future self
Couldn't load pickup availability

Couldn't load pickup availability


